BioCyc Quick Start Guide for New Users
Welcome to BioCyc! Here are some tips to help you get started.Step 1: Select an Organism or Database
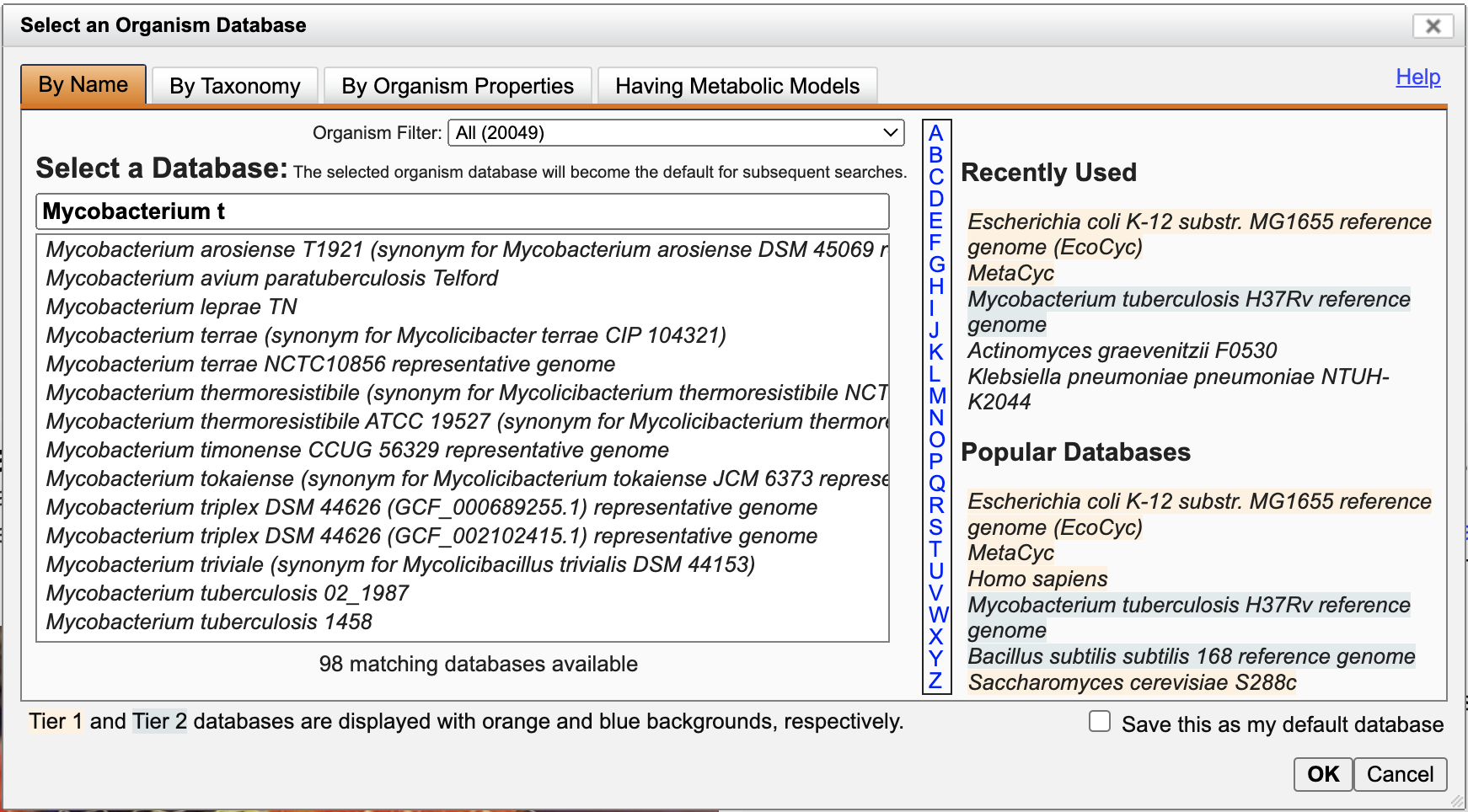
Most searches and other operations apply within the context of a single database: either an organism database or MetaCyc. At the top of most BioCyc pages (including this one) is a section that tells you the currently selected database. If this is not the organism you wish to explore, your first step should be to select your organism of interest using the Change Current Database button.

In the database selection panel that appears, start typing the name of your organism (genus, species or strain). As you type, a list of matching organism names will be shown. Click the one you are interested in. Other options for identifying an organism of interest are given at the the Help link at the upper right of the panel. Click OK to complete database selection. You will be taken to the summary page for your selected database. Your browser will remember your selected database until you change it.
Step 2: What Can I Do Next?
Here are some options for exploring the contents of your selected database:
-
Search
If there is a particular gene, protein, pathway, reaction or metabolite that you are interested in, type its name, accession, or a portion of its name in the Search in Current Database box near the top of every page. If a single match is found, the data page for that object will be displayed immediately. If there are multiple matches, the full list of matches will be shown, organized by the type of object (gene, pathway, etc.). For example, searching for "heme" in Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 generates the following search results. Click on sample result links to explore the different types of pages. Many page types have multiple tabbed sections, be sure to explore them.
There are many other options for different kinds of searches, including searches based on specific properties, searches across multiple organisms, and sequence-based searches. These are accessible from the Search section of the Tools menu at the top of every page. For more information, see the User Guide or our video tutorials.
-
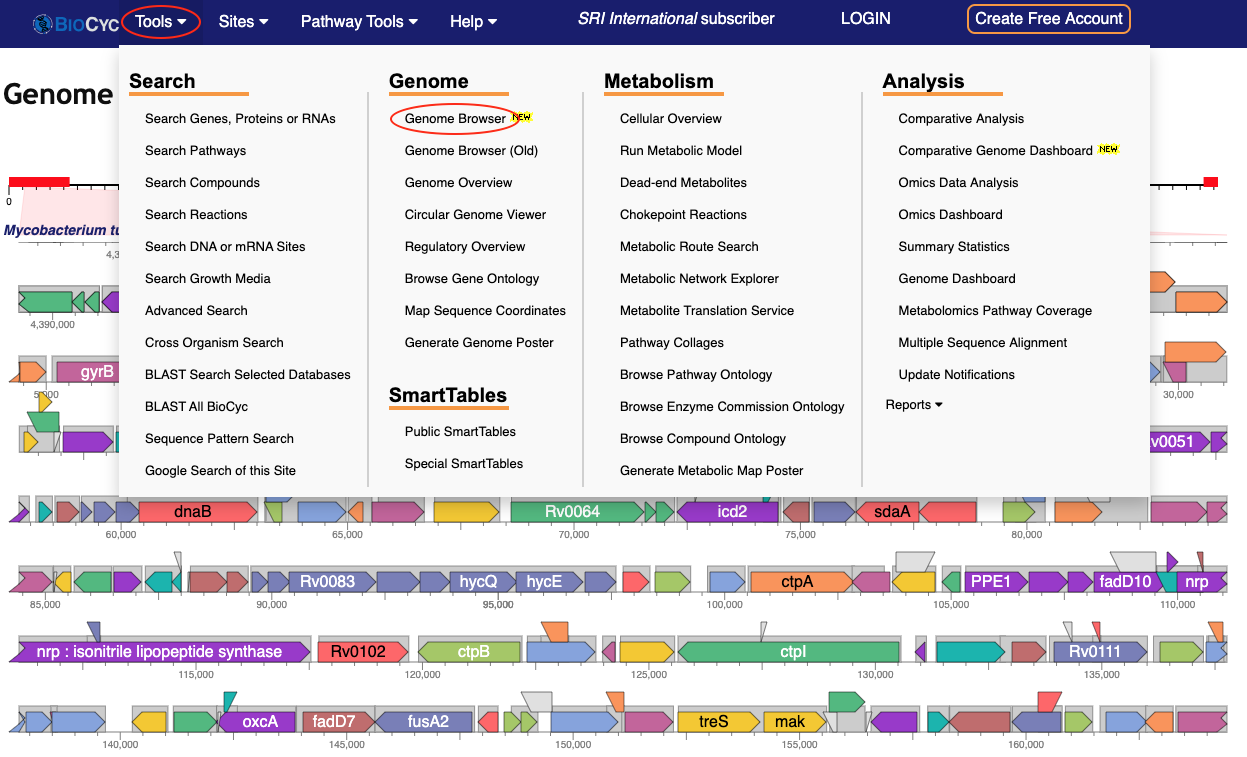
Browse the Genome
To browse the genome of the current organism, select Genome Browser from the Genome section of the Tools menu, shown below. The genome browser is also accessible via a direct link from the BioCyc home page (under the Search box). Use the mouse wheel or trackpad to zoom in or out of the browser, or enter a gene in the search box to center that gene. The Quick Help button will help you get started. For more information, see the User Guide, this short video, or a more in-depth video tutorial.
-
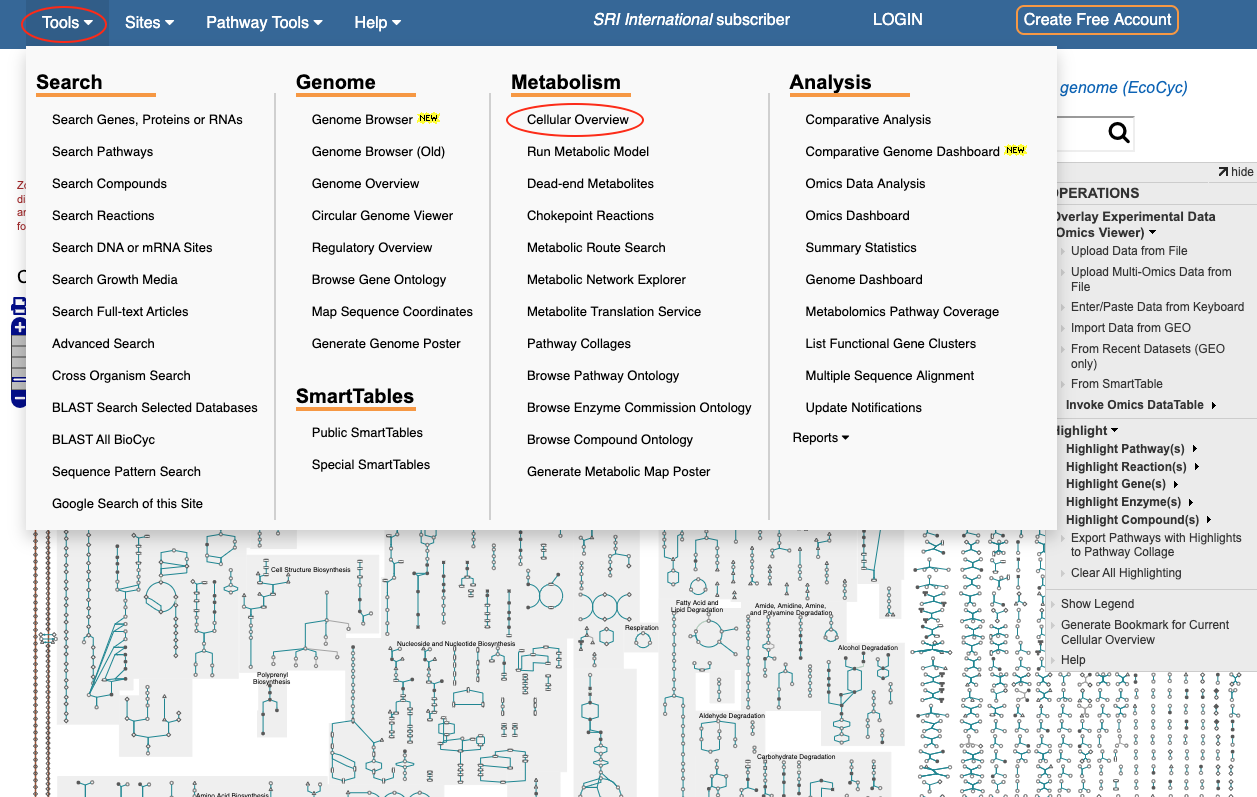
Browse the Metabolic Network
The metabolic network of an organism is depicted in the Cellular Overview diagram, also known as the Metabolic Map. Select Cellular Overview from the Metabolism section of the Tools menu to navigate to this page, or use the direct link labeled "Metabolic Map" from the BioCyc Home Page. The Cellular Overview diagram includes all pathways and metabolic and transport reactions identified in an organism. Use your mouse wheel or trackpad to zoom in for more details, or use the highlight options in the Operations sidebar menu to search for objects of interest. For more information, the Help command in the Operations menu will take you to the relevant section of the User Guide, or watch the video tutorial.
Step 3: Create a Free Account
After some amount of exploration, you will be asked to create an account. We require all users to be logged in to a free account, even if their institution already has a subscription. Creating an account is free, comes with a one-month free trial to all premium BioCyc content, and enables access to advanced features such as SmartTables.
Step 4: Learn More
There are many more tools available on the BioCyc website. The Website User Guide and video tutorials can help guide you. Some topics you might be interested in:- Create, manipulate, and export customized subsets of BioCyc data using SmartTables.
- Analyze and visualize omics data.
- Compare organisms using our comparative analysis tools.
- Execute metabolic models.